Introduction
Cancer clinical trials are studies that are designed to evaluate new treatments or procedures in cancer patients. These trials are a crucial part of the process of improving the current standard of care. Next-generation sequencing (NGS), which can assess a broad range of mutations in multiple genes in a single assay, has emerged as a transformative tool in revolutionizing the design and conduct of cancer clinical trials. By providing comprehensive insights into the molecular profile of tumors, NGS enhances trial efficiency, optimizes patient outcomes, and accelerates drug development.
-
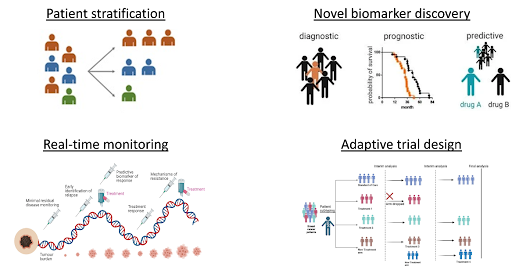
Patient stratification: NGS allows for the identification of specific genetic mutations or biomarkers that may predict a patient’s response to certain therapies. This enables more precise patient selection, ensuring that only those with appropriate molecular profiles are enrolled in the trial. This tailored approach improves the trial’s success rates and ensures that patients receive the treatment that is likely to be beneficial to them, while also reducing unnecessary exposure to ineffective drugs and minimizing potential side effects. For example, a clinical trial looking into targeted therapy for EGFR mutations would prioritize enrolling patients whose tumors harbor EGFR mutations, increasing the likelihood of positive response to the treatment administered.
-
Novel biomarker discovery: NGS can unravel novel genetic alterations that may serve as biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response. Through comprehensive genomic profiling, NGS can identify new biomarkers that may help to predict likelihood of cancer recurrence or progression or predict response to specific therapies. By identifying these biomarkers, their utility can be validated in guiding treatment decisions, improving clinical outcomes, and developing companion diagnostics. For instance, NGS may identify a previously unknown mutation that may serve as a target for a new drug in development, or a new biomarker that may predict efficacy or resistance to an existing therapy.
-
Real-time monitoring: NGS-based liquid biopsies, which analyze circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) from bodily fluids such as blood samples, enables non-invasive tumor monitoring without the need for repeated tissue biopsies. This is particularly useful to track changes in the tumor’s molecular profile over time, assess tumor response towards treatment, and identify emerging resistance mutations. In addition, NGS-based liquid biopsies can also be used to detect minimal residual disease (MRD) in patients who have undergone treatment. Detecting MRD and the small number of remaining cancer cells after treatment, can help identify patients at high risk of recurrence, allowing for earlier intervention.
-
Adaptive trial design: Incorporation of NGS in clinical trials allows for more flexible and adaptive trial designs, which can evolve as the trial progresses. Adaptive trials enable treatment strategies to be modified based on real-time data such as patient’s response, molecular data, and evolving tumor characteristics. Furthermore, since NGS enables more precise profiling and monitoring, the number of patients required in a trial can be reduced and the trial duration can also be shortened, allowing potentially life-changing therapies to reach patients sooner and lowering clinical trial costs without compromising the scientific validity of the results. Integration of NGS into clinical trials represents a paradigm shift by enabling more personalized, effective, and efficient trial designs. It’s ability to identify genetic mutations, monitor tumor evolution, predict treatment responses, and unravel novel drug targets enhances the precision and success of clinical trials. NGS not only improves patient outcomes by selecting the right therapies for the right patients, but also accelerates the development of new cancer treatments. As technology continues to evolve, the utility of NGS in clinical trials is expected to expand, paving the way for more effective and individualized therapies for cancer patients.
Canary Oncoceutics has a steadfast commitment to three fundamental pillars: advancing scientific knowledge, fostering collaboration, and ultimately, enhancing the lives of cancer patients worldwide. From cutting-edge research to impactful clinical advancements, Canary Oncoceutics aims to illuminate the transformative potential of tailored cancer treatments. Join us on this journey towards a future where every cancer patient receives personalized, effective treatment tailored to their unique needs.